Data Scientists Develop Flood Detection for Early Warning
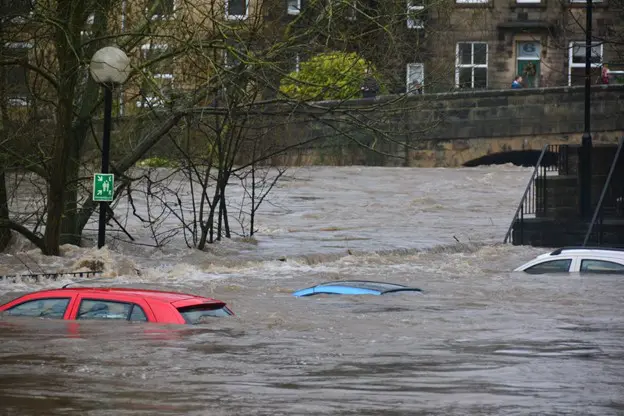

Devastating floods are building headlines throughout the world, but advances in deep understanding for detection could flip uncertainty over evacuations into yesterday’s information.
Implementing a data established of 66,000 photos, data researchers have developed an ensemble of styles for predicting flood zones. And the models are generalizable for software to new geographies.
The findings, printed in a modern paper, will be talked about in a presentation at the NVIDIA GTC 2024 conference following month.
The groundbreaking effort and hard work landed second position at the Emerging Tactics in Computational Intelligence (ETCI) 2024 competitors on flood detection. It came in just a hair guiding, the to start with-put work on what is known as the intersection around union score, or IOU, which steps overlap in impression segmentation.
For Siddha Ganju, one of the paper’s authors, floods are not just some thing you study about or see in viral video clips. When she was 6 a long time outdated, her father was driving in northern India, and his automobile was overturned in a flash flood. He escaped the motor vehicle and was lucky to make it to land alive, swimming past snakes, but he could not contact his family for nearly a working day.
“This was in advance of cell telephones, and we have been waiting for him for a prolonged time,” said Ganju, a senior facts scientist at NVIDIA. “Flooding isn’t like a swimming pool, it is not a little something you can swim by. The recent is extremely quickly and filled with perilous debris like speedy-moving fallen trees.”
India’s monsoon time can hammer rainfall of 3 ft or additional all through a working day, all of a sudden bursting rivers with a tsunami-like power of h2o. Earthquakes can prompt unexpected flooding as effectively.
Floods trigger more than $40 billion in damages globally a yr, according to the Corporation for Financial Cooperation and Growth.
Flood Segmentation in Seconds
The ETCI opposition questioned contestants to use 66,000 SAR Sentinel-1 labeled photographs with pixels that exhibit prior to and immediately after a flood. Participants had been challenged to create semantic segmentation products employing the information so that they could be applied to new unlabeled photos to accomplish inference on opportunity flood zones.
The photos — supplied by NASA’s Interagency Implementation and Superior Ideas Staff — bundled Bangladesh Nebraska North Alabama Purple River, North Dakota Florence, North Carolina and other regions.
Ganju teamed up for the ETCI opposition with Sayak Paul, a machine learning engineer at e-commerce startup Carted. The benefits confirmed that their designs, operating on NVIDIA V100 Tensor Main GPUs, can generate a segmentation for flood zones spanning about 24,000 square miles in just 3 seconds.
Education Product Ensembles
Ganju and Paul formulated an ensemble of models with UNet and UNet++, a pair of convolutional neural community architectures employed for image segmentation. They can assess pixels for borders in between items like land and water.
The duo’s ideal performing model was qualified in various iterations, with the output of each individual stage feeding into the upcoming phase.
NVIDIA V100 GPUs in the cloud powered the instruction for the ensemble of models, and all the inference was carried out on them as perfectly.
Acquiring for Social Influence
Their generalizable technique can be conveniently applied. Unique illustrations or photos of annotated coast strains, deserts, urban places or many others aren’t needed, as it’s all built into the product. This permits other individuals to harness the get the job done for any location, probably just updating the data set to strengthen it with transfer discovering.
Ganju and Paul hope their code, posted on GitHub, is picked up by area gurus in science disciplines who can strengthen and deploy it for emergency systems around the environment. They are in talks with the United Nations Satellite Centre, which is intrigued in testing the AI to enhance its flood detection instrument and disaster response procedure, explained Ganju.
“A lot of persons could be instantly or indirectly impacted by this,” she reported.
Originally posted 2021-11-11 12:56:41.